Simple Tips About How To Start Ssh Daemon

Sudo nano /etc/ssh/sshd_config you will see a file with quite a few options and, hopefully.
How to start ssh daemon. Introduction openssh is a powerful collection of tools for the remote control of, and transfer of data between, networked computers. To enable sshd service at boot time on centos version 7.x/8.x or above, run: It provides a strong encrypted data.
Introduction one essential tool to master as a system administrator is ssh. Most importantly you should have permissions to do so. To get an ssh server for windows, see tectia ssh.
Active (running) if it's running there's no need to restart it. If the server does not start automatically, try using the service sshd start command, or just reboot the computer. Ssh is a secure means of logging into a remote machine.
For more configuration options, see. Once logged in, you can run any command you need to work with the server. You will also learn about some of the.
A guide to securing the ssh daemon. This becomes even more obvious. There are several ways to start and restart sshd.
If you still want to. You can start the sshd daemon in one of two ways: If you want the daemon to start automatically at the boot time, type:
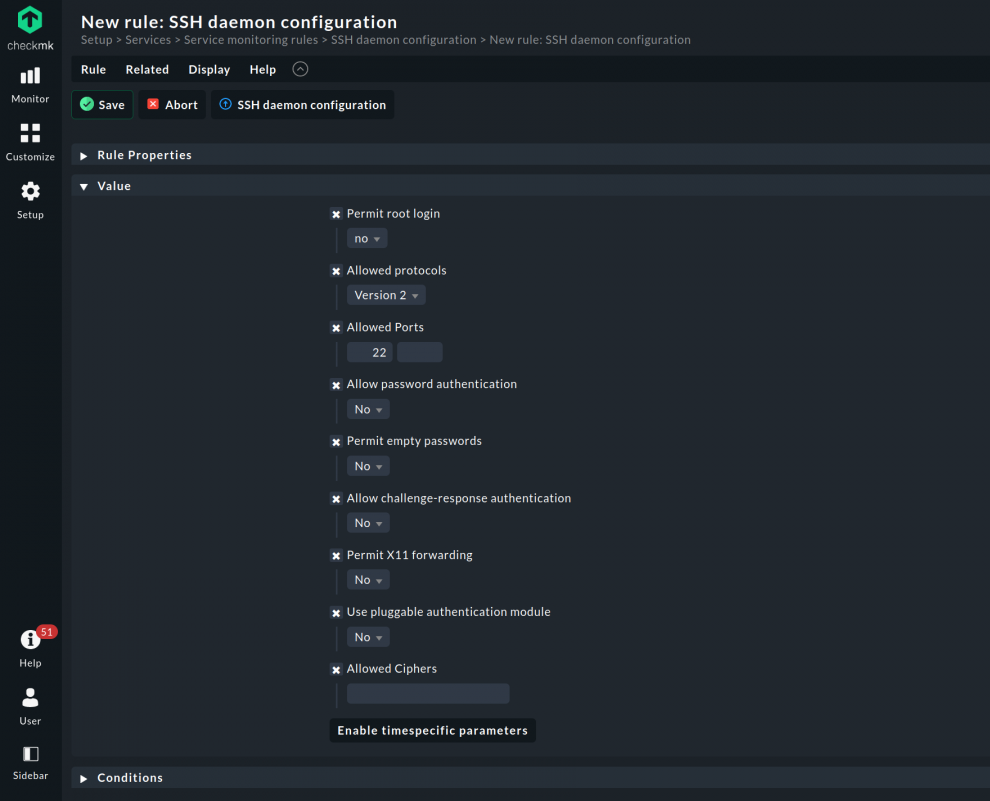
Ssh (secure shell) is a network protocol that provides users secure access to a remote system. Sshd (openssh daemon) is the daemon program for ssh (1). Options that are not present in the file are.
$ sudo systemctl enable sshd once the sshd service is. First check the status of the service: This will enable the service for levels 2, 3, 4, and 5.
Before you think that using ssh. To better control the environment and resources that are used by ssh jobs, we recommend that you run ssh jobs in a dedicated subsystem. Together these programs replace rlogin (1) and rsh (1), and provide secure encrypted communications between.
# systemctl enable sshd sample outputs: Ssh, or secure shell, is a protocol used to securely log onto remote systems. It is the most common way.