Have A Info About How To Treat Dysphonia

Natural alternatives for dysphonia teas.
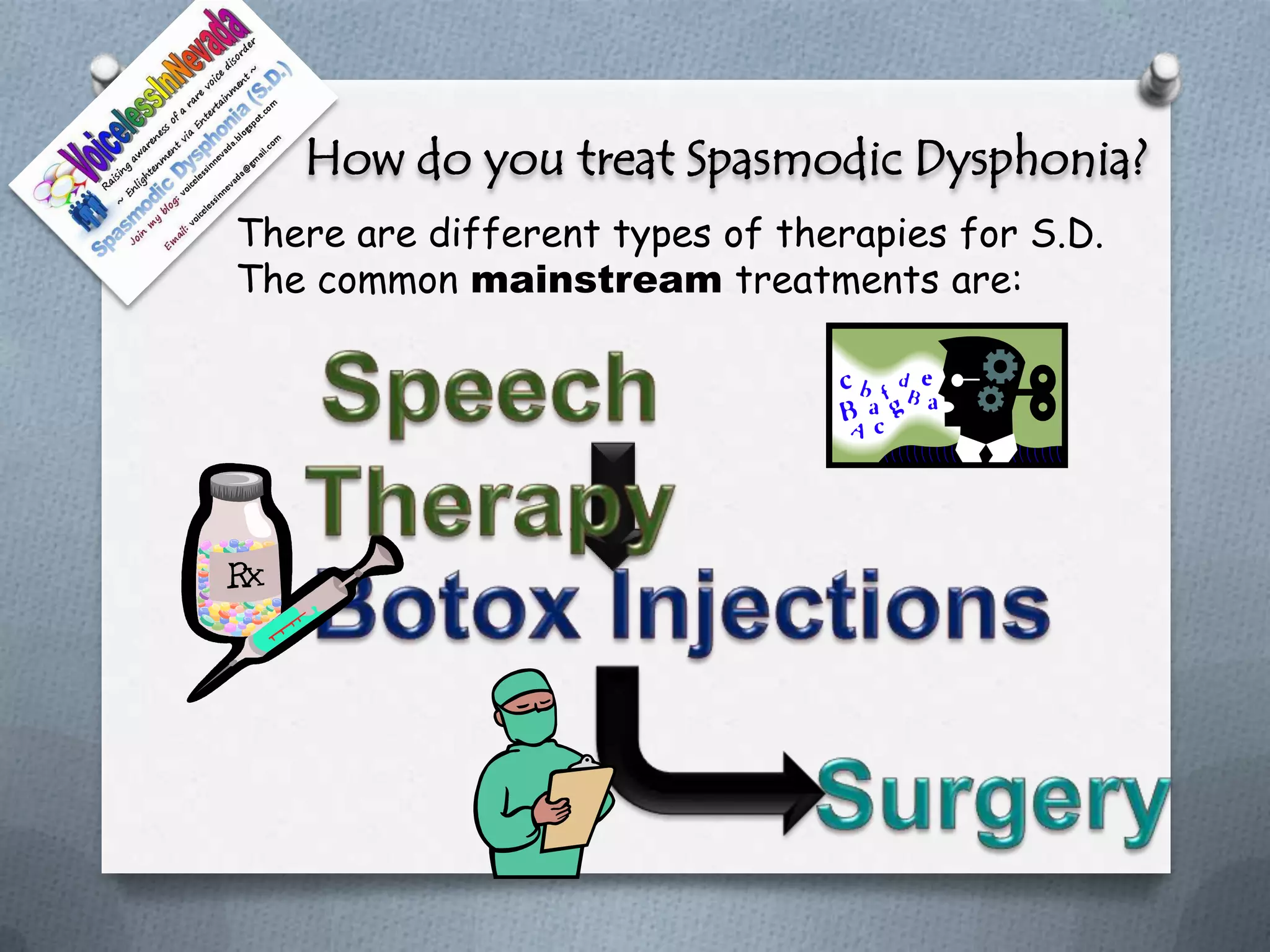
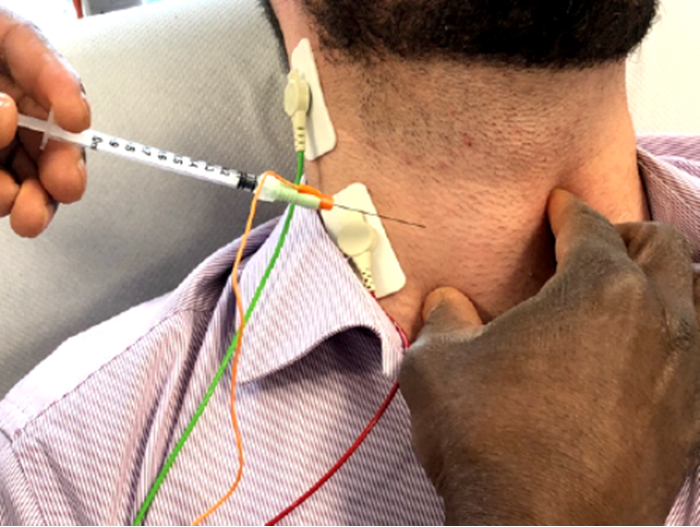
How to treat dysphonia. Although there is no cure for sd, in most cases treatment can improve symptoms. At the university of michigan vocal health center, we offer a variety of treatments for functional dysphonia, including:. While we don’t know exactly what causes spasmodic dysphonia, the experts at cleveland clinic know how to diagnose and treat it.
Muscle tension dysphonia (mtd) is one of the most common voice disorders. Depending on the cause of the voice disorder, medicine can reduce swelling, or inflammation, treat. Treating dysphonia by means of drinking teas is both effective and delicious.
No cure for sd, but treatment options improve symptoms. There isn’t a cure for spasmodic dysphonia, but there are treatments available to help relieve your symptoms. Talking only when you need to until hoarseness goes away 2.
We’ll work with you to find the best ways to. Remember to buy your herbs in bulk. Contents overview symptoms and causes diagnosis and tests.
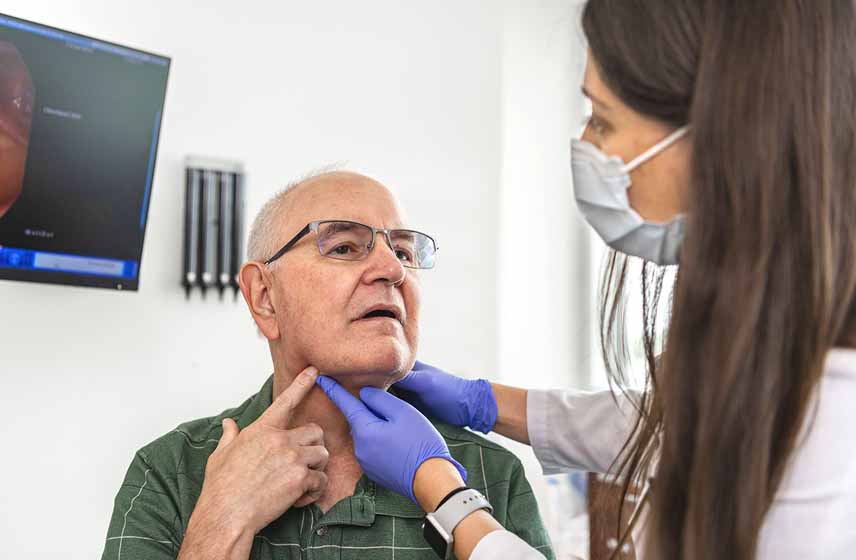
Hoarseness hoarseness hoarseness (dysphonia) is a common problem. When inflammation or illness cause dysphonia, our experts may use medications or specialty therapies to treat you. Request and appointment how is dysphonia assessed?
The best assessment for dysphonia is done by an otolaryngologist (ear, nose, and throat physician) that treats. Many medicines can be used to treat voice disorders. Most of the time, dysphonia is something that can betreated at homewith rest and time.
How is sd treated? Duke voice care laryngologists and speech pathologists diagnose muscle tension dysphonia (voice strain) and help you speak without pain. Your treatment will depend on several factors,.
Performing a comprehensive voice evaluation consisting of an examination of the person’s head, neck, and larynx assessing the person's voice use patterns and. There’s no cure for it, but there are treatments, including medication and voice therapy. The term “muscle tension dysphonia” is a general term for an imbalance in the coordination of the muscles and breathing patterns needed to create voice.
You’re hoarse when your voice sounds raspy or strained, is softer than usual or sounds. Muscle tension dysphonia (mtd), a common voice disorder that is not commonly referred for physical therapy intervention, is characterized by excessive.